Tax Operations Procedures Mainfreight 2022
Introduction
PurposeTo meet the Board’s expectation in the Tax Policy, this document outlines how Mainfreight Group’s tax obligations are met from a compliance and risk management perspective. |
ContextThis document forms part of the Tax Governance Framework. The diagram below demonstrates the key components of the Tax Governance Framework: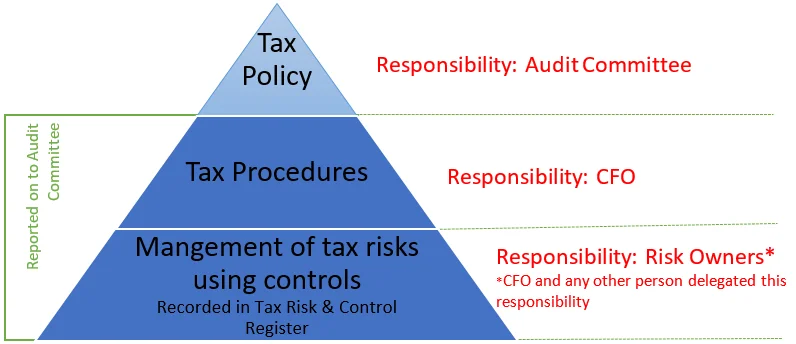 |
ScopeThese procedures govern both payroll and non-payroll taxes. |
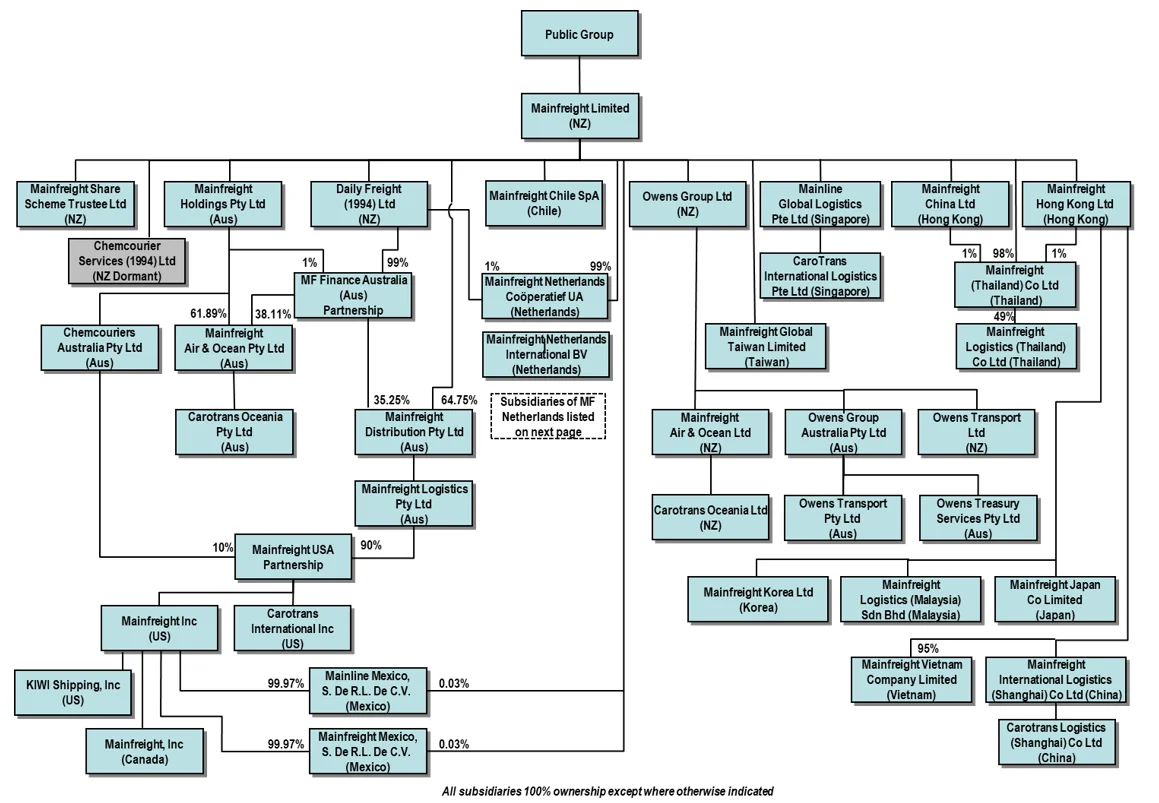
ApplicationThis document applies to all entities in the Mainfreight Group (refer to Appendix One for structure diagram), including the Board, the Audit Committee and all employees with roles that could have tax consequences. |
Routine tax complaince
ResponsibilitiesThe tax compliance roles and responsibilities and signing authority for each of the tax types and Group entities is outlined in Appendix Two. |
External advisorsWhere required, external advisors should assist in the preparation and lodgement of returns.External advisors must be used to:
|
Independent ReviewA 12-month sample of data should be reviewed using data analytics by an external advisor at least every five years for entities / tax types:
|
Tax risk management
Identify tax riskRisk owners[1] and external advisors should identify events, actions or inactions which may present a tax risk and bring these to the attention of the Chief Financial Officer.The events, action or inaction that may present a tax risk include:
|
Evaluate tax riskOnce a tax risk has been identified, the Chief Financial Officer should assess the tax risk as either a routine or significant tax risk taking into account the impact that the tax risk could have and the likelihood of that tax risk eventuating.Routine tax risks are tax risks that arise on a regular basis in the ordinary course of business with no unusual complexity or are consistent with historic tax positions. Significant tax risks arise outside of the ordinary course of business or have a higher degree of complexity or uncertainty. Factors that indicate a significant tax risk include:
|
Determin tax risk treatmentOnce a tax risk has been evaluated, the Chief Financial Officer (assisted by external advisors, if required) should assess the options available for the treatment of the tax risk which include:
|
Determine whether the tax risk should be escalatedIf, after controls are implemented:
|
Implement and monitor controlIf the tax risk is accepted and controls are implemented, the Chief Financial Officer is responsible for implementing and monitoring the effectiveness of the control. |
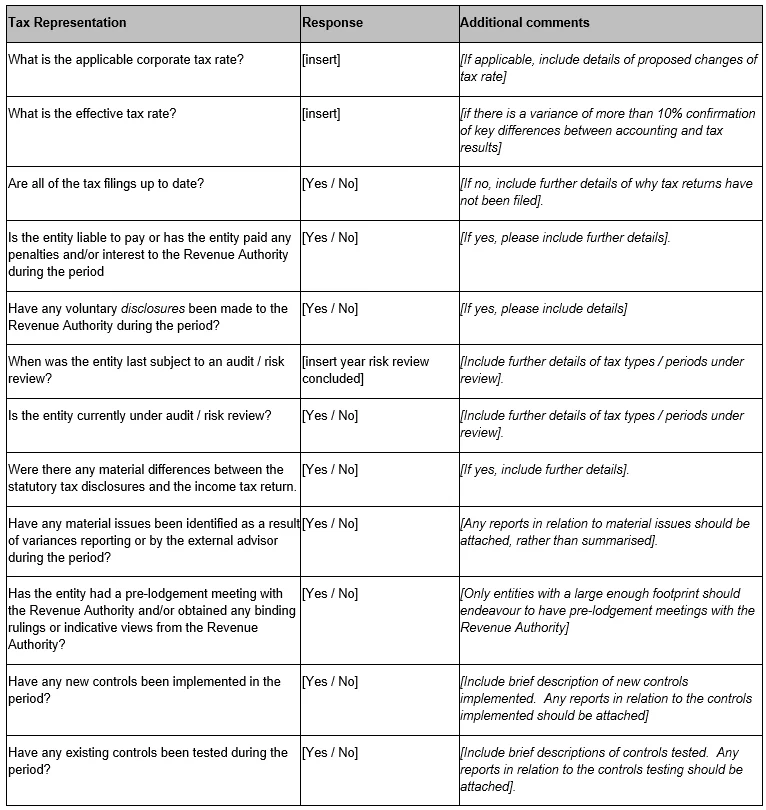
Reporting to the Audit CommitteeAt least annually, a Tax Status Report (refer to Appendix Three) should be prepared for each country that Mainfreight Group operates in. |
| [1] A Risk Owner is the CFO or anyone the CFO has delegated responsibility for the implementation of a control. In practice mainly regional Financial Controllers. [2]A ‘more likely than not to be correct opinion’ will support the merits of tax treatment of an item if challenged. In numeric terms, a more likely than not to be correct tax position has a 51% (or greater) chance of occurring. [3]A should opinion supports the merits of tax treatment of an item to the extent that although not entirely free from doubt, the taxpayer's position should prevail. In numeric terms, a Should Opinion can be obtained where there is at least an 80% likelihood that the tax treatment of the item will be upheld if challenged |
Tax compliance & tax risk reporting
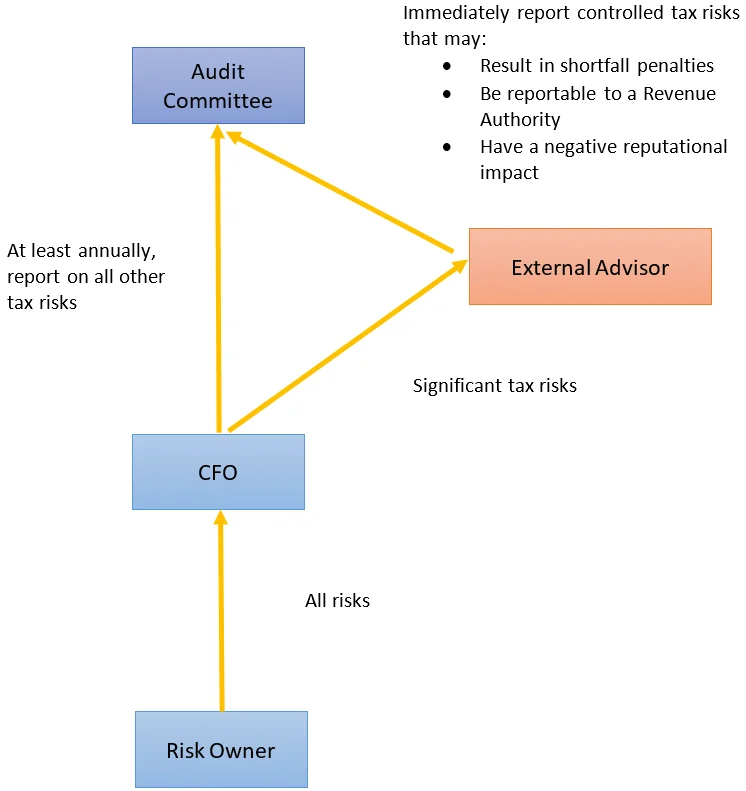
External Advisors
When to engageExternal advisors should be engaged to assist with the management of taxes as required, however, must be engaged to assist with the management of any signficiant tax risks. If matters are particularly complex, sensitive or material, a second opinion from an accounting or legal firm or Counsel’s opinion can be obtained. |
Who to engageWhere possible or practical, external advisors from a ‘Big Four’ professional services firm should be engaged at regional level. When deciding which external advisors to engage, consideration should be given to whether the matter requires an advisor with specialist and/or industry knowledge. |
Level of opinionWhere there is a significant tax risk, an opinion should be sought from external advisors. If a tax position to be taken:
|
Additional SupportIn addition to seeking an opinion from external advisors, additional support may need to be maintained in relation to the tax position. Options available include:
|
Stakeholder relationships
Revenue AuthoritiesAssisted by external advisors, the Chief Financial Officer should determine how to maintain an open, honest, and co-operative relationship with Revenue Authorities taking into account the size of the business in that jurisdiction. Options available may include:
|
Other stakeholdersThe Chief Financial Officer must review the tax disclosures made in the annual report prior to finalisation. |
Training and awareness
External TrainingTo keep up to date on tax matters which could impact Mainfreight Group, the Chief Financial Officer, Finance Team and Payroll Team should regularly attend external tax trainings. |
Internal TrainingTo cascade knowledge across the business and promote ownership of tax governance, the Chief Financial Officer, Finance Team and/or Payroll Team should provide an annual tax update to the business. |
Document management
Tax recordsTax records in accordance with statutory obligations in each jurisdiction should be centrally maintained. Where a tax event spans over several years, the tax record should be maintained for at least the minimum statutory period from the end of the tax year affected by the tax event |
Drafts / finalsGenerally, if the final version of a tax record can be located, draft tax records should not be retained. However, drafts should be retained where it supports a tax position taken or evidence intentions (for example, where a third party has requested the draft tax record be amended). |
ProtectionsDocuments that are subject to a non-disclosure right or legal professional privilege should be clearly marked as such.Papers to the Audit Committee should not include summaries of tax advice received. Rather, the paper should state that tax advice has been received and a copy of that advice should be attached. If summaries of advice are required, the external advisor should prepare the summary. Before any tax document that is requested by a Revenue Authority as part of a risk review or audit is made available to a Revenue Authority or a third party, the document should first be reviewed by external advisors. |
DestructionPrior to destroying any tax record, consideration should be given to:
|
Administration of Procedures
ImplementationThese Procedures will be implemented by:
|
ReviewThese Procedures should be reviewed annually by the Chief Financial Officer who will propose any changes, if appropriate, to the Audit Committee. |
ComplianceCompliance with these procedures will be assured through:
|
Point of contactThe Chief Financial Officer is the point of contact for matters arising in relation to the Procedures. |
Appendix One: group Sturcture Diagram
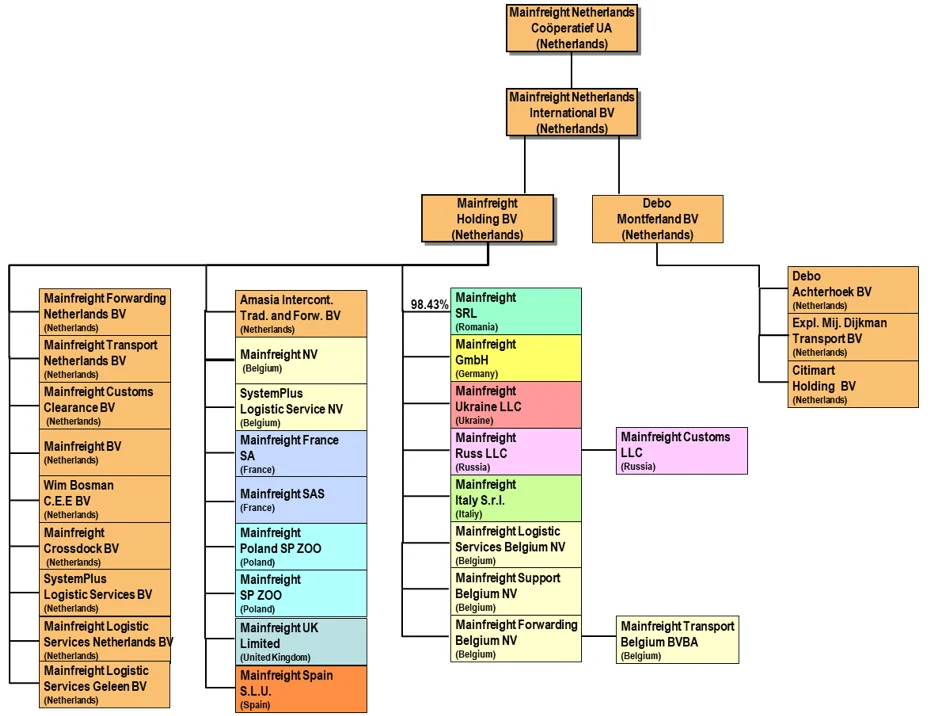
Subsidiaries of Mainfreight Netherlands
Appendix Two: Roles & responsibilites
Overview of Responsibilities
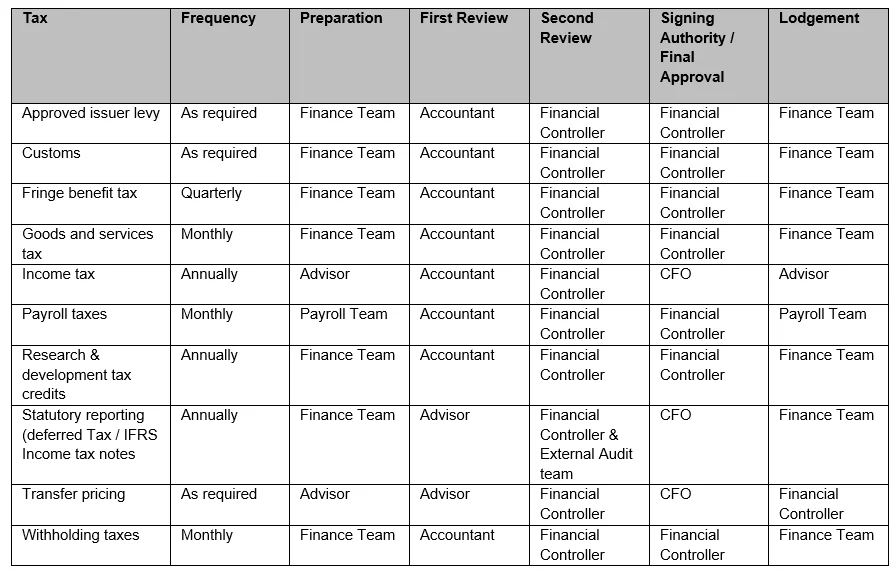
Specific responsibilities
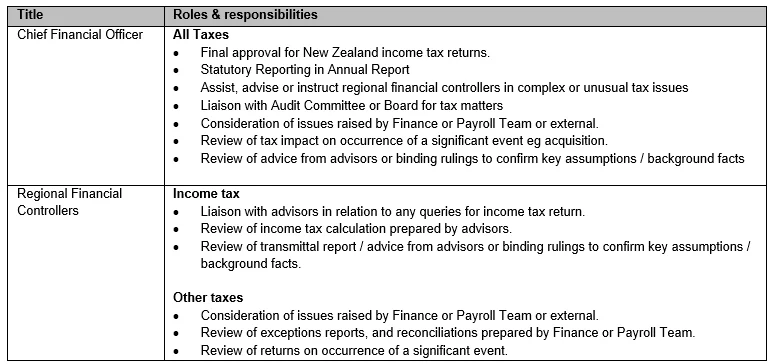
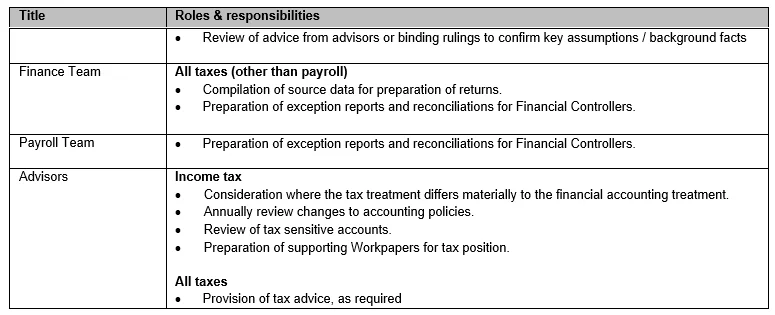
IT Systems
The following IT system(s) are used to fulfil the roles and responsibilities described above:- Accounting and operating systems used to capture all transactions including tax
- Transport – On Account (accounting system) & Mainstreet (operating system)
- Warehousing - On Account (accounting system) & MIMS (operating system)
- Air & Ocean – CargoWise (accounting & operating system)
Appendix Three: Tax Status Report
| Entity/ies | |
| Country | |
| Period | To be filled with annual CBCR report |
| External Advisor | |
| Status of Report | Subject to non-disclosure right or legan professional privilege |

Download
Tax Operations Procedures | Mainfreight 2022
To meet the Board’s expectation in the Tax Policy, this document outlines how Mainfreight Group’s tax obligations are met from a compliance and risk management perspective. Download to read more
